Android devices now provide much greater battery optimizations than ever before. From providing a much powerful battery saver mode to background restrictions and the Adaptive battery feature, all these prove to be of considerable help for your device’s battery. But many users are still in the dark when it comes to the Standby app on Android devices. And we can’t blame them either. The feature is so hidden deep inside the Developer options that it is hard to get your eyes on it. Well, today we are going to each and every detail of these Standy Apps. We will also have a look at different available modes of the Standy apps and the steps to switch between them.
Standby Apps on Android
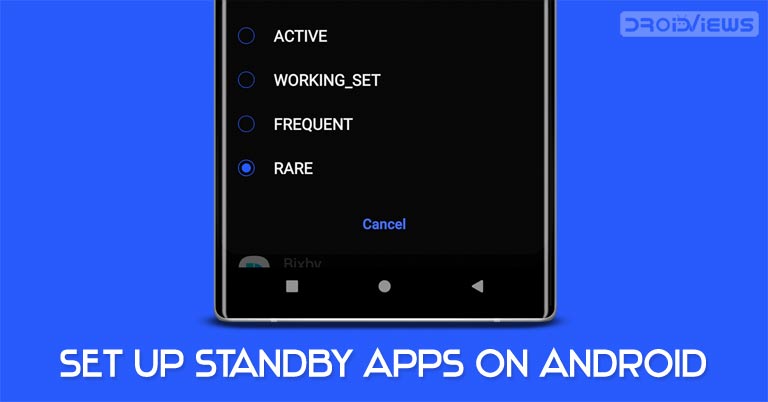
Standby Apps isn’t a name given to any particular set of apps. Rather, it is a Developer Mode feature that manages battery and resource utilization of all the user-installed apps. It segregates your apps into four different standby categories, with each placing more battery and CPU usage restrictions on your apps than the former. The four different modes include Active, Working_set, Frequent and Rare. Let’s have a look at each of these sets.
Available Standby Apps Modes Explained
- Active: This Standy App mode imposes the least restriction among all the available ones. Android System will not place any restrictions whatsoever in the app’s ability to perform its job or trigger alarms (or notifications). Likewise, internet access isn’t restricted while the apps are in their active states.
- Working_set: Jobs may be deferred up to 2 hours and alarms up to a maximum of 6 minutes. However, there is no restriction on network connectivity.
- Frequent: Jobs may be postponed up to 8 hours and alarms up to 30 minutes in this Standby Apps mode. As far as the internet is concerned, there is no restriction imposed here as well.
- Rare: The strongest of all the four modes. Jobs are deferred up to 24 hours. Moreover, alarms are also deferred, with a maximum time of up to 2 hours. In this category, there is also a network restriction imposed, which stands out at a maximum of 24 hours.
Other Modes
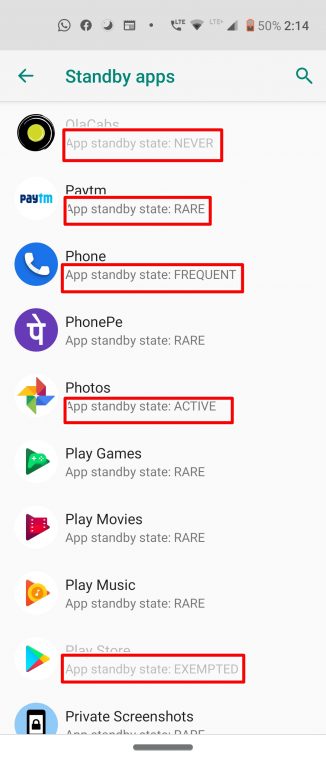
Some other Standby Apps modes may include Never and Exempted. Apps like Google and Play Store are altogether Exempted from the Standby App feature. Others like the Home app from Google or the Assistant App belong to the Never category. You cannot perform any action on apps belonging to these two modes.
Moreover, as is evident from above, the restrictions get tighter as one moves from the Active state to the Rare one. Likewise, if you want more information on this topic, you could head over to the Android Developer website on this very topic.
So this was all about the four different modes of the standby apps. But how to enable them in the first place? Well, below are the instructions to do so on your respective Android devices. Moreover, steps regarding the switching of modes for each app is also provided.
Enabling and Switching Modes
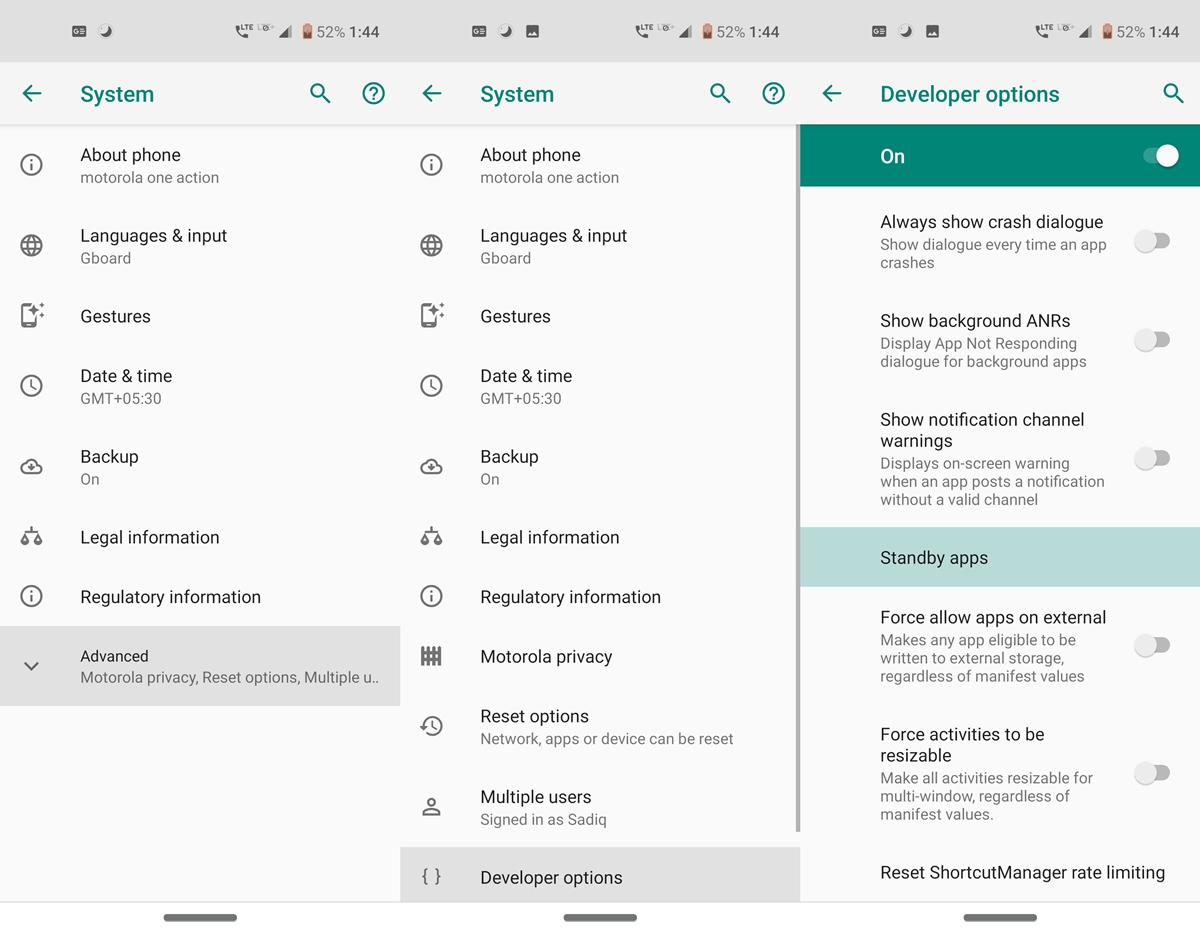
To enable the Standy Apps feature, start by turning on the Developer options on your device. To do so, go to Settings > System > About phone and tap on Build number 7 times. Then go back to the System and tap on Advanced. Developer Options will now be present there. Scroll to the bottom and Look out for the Standby Apps feature. You may also take the help of Setting’s Search bar. That’s it. You could now see all the user-installed apps along with their default state.

The standby apps default state is mentioned just beneath the app’s name. To change their respective states, just tap on the Android app’s name. From the list, select Active, Working_Set, Frequent or Rare, as per the need. However, it may happen that switching to any of these modes may make the app behave rather unexpectedly. If that’s the case, consider switching them back to their default state. Once you are done with setting up the Standby apps’ modes, you can now turn off the Android Developer options.
With that, we conclude the guide on Standby apps on Android. Are you going to try out this feature? Or the regular battery saving and optimization features are more than sufficient? Let us know in the comments below.
Read Next: How to Get Faster Data Speed on Android


Join The Discussion: