
If you’re an Android enthusiast, you’ve most probably heard of ADB & Fastboot. If I had to bet I’d bet that you’ve most probably even used them. Android is very customizable but there are certain things that you still can’t do without root access. Yet, there are certain things that you can do without root access but you need ADB & Fastboot. From backing up your device to changing screen resolution or even flashing custom recoveries, unlocking the bootloader, ADB and Fastboot have a lot of uses. We’ve seen how you can install ADB & Fastboot on Windows before. Windows isn’t the only desktop OS around though. There are several others based on Linux, just like Android. Here’s how to setup or install ADB and Fastboot on Linux.
Download ADB for Linux
The best way to install ADB and Fastboot on Linux or any other OS would be to install the Android SDK Tools. It comes with ADB and Fastboot bundled and is also regularly updated by Google. You can download the zip from the download link below.
How to install ADB and Fastboot on Linux
- Extract the downloaded zip file to an easy to access location such as the desktop. This downloaded folder contains all the files necessary to run ADB & Fastboot and requires no further installation. To use ADB & Fastboot though you will need to access this folder from a Terminal.
- Open the Terminal by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T or via whichever app launcher or method you prefer.
- In the Terminal, access the extracted folder by using this command:
cd /path/to/extracted/folder/Replace /path/to/extracted/folder/ with the actual path to the folder. For instance,
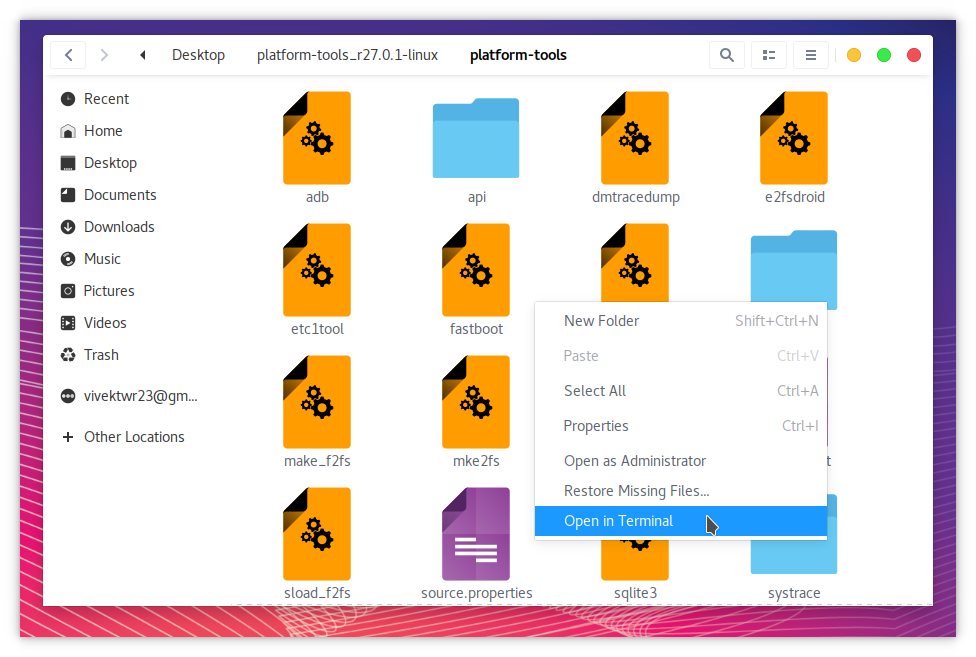
cd /home/username/Desktop/platform-tools_r27.0.1-linux/platform-toolsAlternatively, you can open the folder using Nautilus, which is the default file manager on most Linux distros, right-click on an empty area and select Open in Terminal.
- Connect your Android device to your Linux PC with a USB cable now. On your device select the MTP file transfer mode. Some devices allow ADB to function without an MTP connection but unless you’re sure your device is one of those, it is safe to go with the MTP file transfer mode.
- In the Terminal, enter the following command and it will trigger a prompt on your connected Android device.
adb devices
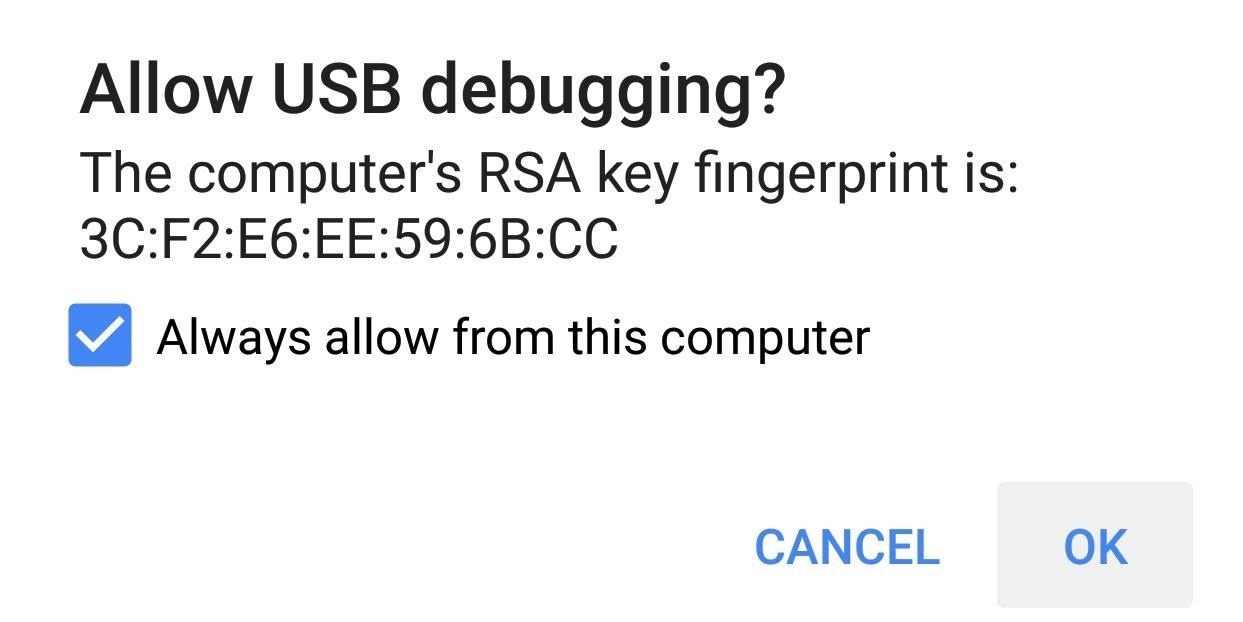
- On your Android, you should see a prompt asking you to allow USB debugging permissions to the connected PC. Go ahead and grant it.
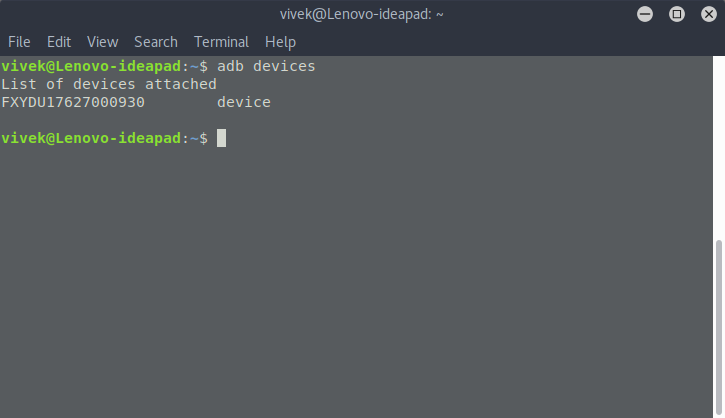
- Repeat the command given above and you should now see your device listed along with its serial number.
Add ADB & Fastboot system-wide (Optional)
- In a Terminal, enter the following command to open the .bashrc file in a Text editor of your choice. The command below will open the file in gedit.
sudo gedit .bashrc
- At the end of the file, add the following line then save and exit.
export PATH=${PATH}:/home/YOUR-USERNAME/path/to/adb - In the Terminal, type adb to see if ADB still works. If it doesn’t, which is possible on 64-bit systems, install the packages glibc.i686 and libstdc++ and it should work.
Install ADB & Fastboot via Terminal commands
While the above method will work for every Linux distro, it is not the best way to install ADB & Fastboot on all Linux distros. Some Linux users can have a more hassle-free, system-wide ADB & Fastboot installation. Users who have a Debian or Fedora/SUSE-based distro of Linux need not download the above linked platform-tools folder. Simply launch a Terminal and enter one of the following commands depending on the Linux distribution you use.
- Debian-based Linux users can type the following command to install ADB:
sudo apt-get install adb - Fedora/SUSE-based Linux users can type the following command to install ADB:
sudo yum install android-tools
For the uninitiated, Ubuntu, the most popular Linux distribution and its various official flavors and derivatives are all Debian based. Also, while Ubuntu users need not worry, there’s one other thing that you should keep in mind if you’re using other Linux distributions. If you’re using such a distribution, you probably already know but you may have to type a ./ before every ADB command. For instance, the adb devices command used above should be typed as below.
./adb devices



Join The Discussion: