
You must have heard about ARM, ARM64, and x86 processors that power most modern smartphones. Which of these processors your Android has, which of them is better, and what’s the difference between ARM, ARM64, and x86? We’ll try to answer all these questions!
Starting with Android 5.0 Lollipop, Google added support for 64-bit processors on Android. It was then that knowing your processor became something pretty important for many people. Whether you have a 32-bit processor or 64-bit processor can decide which custom ROM or GApps you can install. It also decides which version of an APK you choose to sideload an app, the version of Xposed Framework and many other things as well. Then there are differences between processors based on the ARM architecture and those based on the x86 architecture too. So what’s the difference between ARM and x86 processors?
What’s the Difference Between ARM, ARM64, and x86?
ARM Processors
ARM is usually the architecture used to build a CPU for a mobile device. Processors based on ARM (32 bit) follow a follow a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) architecture. In fact, ARM itself stands for Advanced RISC Machine. What it boils down to is that ARM processors are simpler to make and thus cheaper. Most instructions are simple and execute in one clock cycle. There are many technical details that we can get into but all of them will mostly fly over the head for most people unless you are a professional in this field.
If you have a smartphone or any mobile device that depends mostly on battery life for functioning, it probably uses an ARM-based processor. These processors are generally a lot better in comparison to x86 when it comes to power consumption. While processor performance also depends on a lot of other factors such as cache, bus width, etc., ARM processors are usually less powerful in comparison as well.
ARM64 Processors
Although laptops do require low power consumption, they have been around long before ARM actually became a viable option. Desktop grade operating systems and apps, such as Windows 10 and the desktop version of Chrome requires a lot more power to work smoothly. Back then, ARM processors couldn’t provide such processing power but things are changing. ARM64 is simply an extension or evolution of the ARM architecture that supports 64-bit processing.
64-bit processing is far superior to 32-bit, and thus, ARM64 processors tend to perform better than ARM processors. Microsoft has been working with ARM to make Windows 10 possible on ARM-based processors, they’ve even released a few devices under the Windows 10 on ARM program. Windows has always been a desktop OS and hence has always only supported x86 (x64) architectures. Although, with longer battery life, ARM-processors provide the opportunity for devices to stay connected (or at least stay on) all the time. Microsoft has made clear that it sees the future is 2-in-1 devices that can act as a laptop and tablet both. Thus, the push for Windows 10 on ARM.
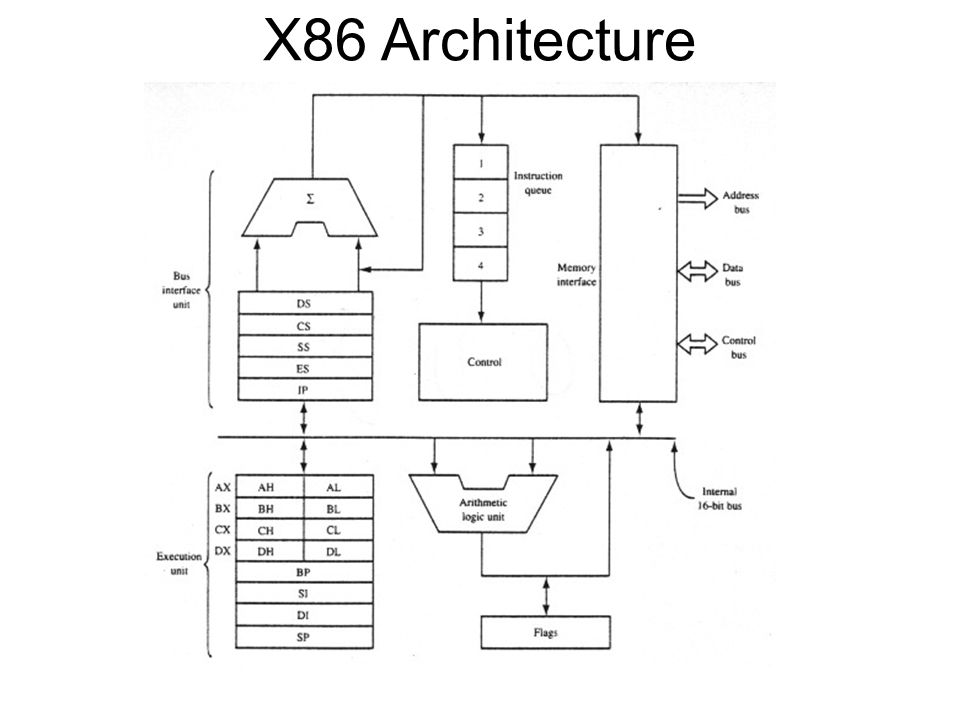
x86 Processors
x86 is a whole different architecture made popular by Intel. Processors made using the x86 architecture are generally used on desktops and laptops. Even AMD, Intel’s rival in desktop and laptop processors uses Intel’s x86 and x64 (which is a 64-bit version of the x86 architecture) architectures to create their CPUs. Processors based on the x86 follow a CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) architecture. Instructions on x86 processors are mostly complex. Thus, they take up multiple CPU cycles to execute each instruction.
Intel has worked hard to make these processors as power efficient as they could but x86 is, by design, just not as battery-friendly as ARM. Although some Android devices do run on Intel Atom processors based on the x86 architecture. Some examples would be the Asus Zenfone, Zenfone 2, Lenovo K80, etc. While ARM processors have become powerful enough to run full-fledged desktop operating systems like Windows 10, they’re still far behind.
These architectures have existed since the 90s in parallel worlds. ARM has always been for the low-power mobile devices such as phones and small PDA. x86, on the other hand, has always been the processor architecture that provided more power, by using more electricity, suitable for desktops. Even if in the next 5 years, ARM becomes the go-to processor architecture for laptop processors, it probably will never be able to compete with x86 on the desktop, which will always be more powerful, and thus, more suitable.
This is all I have to say about the difference between ARM, ARM64, and x86 for now. With a hope that this article helps you understand the processor used in your Android device, I wind up. Cheers!


Join The Discussion: